Soma cube
The Soma cube is a mathematical puzzle by Piet Hein.
- This text is from the 'Tetromino' article, and is being edited
Counting rotations in two dimensions as equivalent, there are seven possible shapes:
 I (also called "stick", "straight"): four blocks in a straight line
I (also called "stick", "straight"): four blocks in a straight line Square (also called "O", "package", "block"): four blocks in a 2x2 square
Square (also called "O", "package", "block"): four blocks in a 2x2 square T: a row of three blocks with one added below the center
T: a row of three blocks with one added below the center
A common move with the T piece is to spin it in place to fill a line. L: a row of three blocks with one added below the left side
L: a row of three blocks with one added below the left side J (also called "inverted L", "Gamma"): a row of three blocks with one added below the right side
J (also called "inverted L", "Gamma"): a row of three blocks with one added below the right side
This piece is a reflection of L but cannot be rotated into L in two dimensions; this is an example of chirality. However, in three dimensions, this piece is identical to L.) S: bent trimino with block placed on outside of clockwise side
S: bent trimino with block placed on outside of clockwise side Z: bent trimino with block added on outside of anticlockwise side
Z: bent trimino with block added on outside of anticlockwise side
Reflection to S. See "J", above.
When added the third dimension, there are three more patterns, all created by placing a unit cube on the bent trimino:
 Left screw: unit cube placed on top of anticlockwise side. Chiral in 3D.
Left screw: unit cube placed on top of anticlockwise side. Chiral in 3D.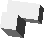 Right screw: unit cube placed on top of clockwise side. Chiral in 3D.
Right screw: unit cube placed on top of clockwise side. Chiral in 3D. Branch: unit cube placed on bend. Not chiral in 3D.
Branch: unit cube placed on bend. Not chiral in 3D.
See also:
